

Overview
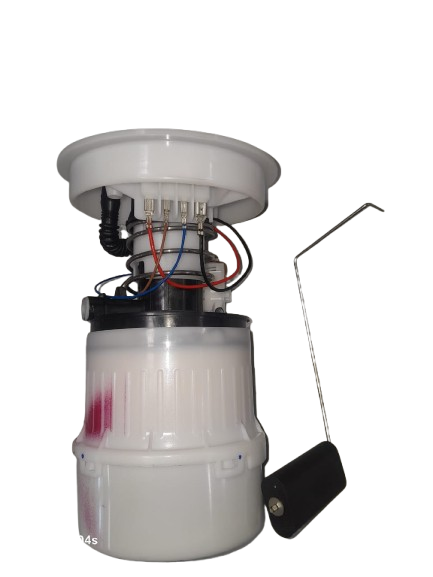
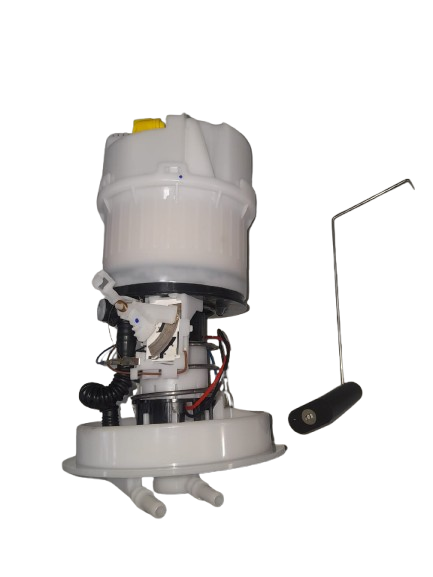
The fuel pump is a critical component of modern vehicles, including popular models such as the Mazda 3, Ford Focus, and various Volvo cars. Its primary function is to deliver fuel from the tank to the engine at the correct pressure for efficient combustion. These vehicles generally employ electric fuel pumps, which are integrated within the fuel tank (in-tank type) to ensure consistent performance, noise reduction, and improved safety.
Design and Construction
The fuel pump assembly typically consists of several key components:
- Electric motor – drives the pump mechanism.
- Pump impeller or turbine – pressurizes the fuel.
- Pressure regulator – maintains optimal fuel pressure.
- Fuel filter and strainer – remove contaminants from the fuel.
- Fuel level sensor – measures and transmits the fuel level to the dashboard gauge.
In the Mazda 3 and Ford Focus, which share certain design similarities due to historical engineering collaboration between Mazda and Ford, the fuel pump module is compact and integrated with a returnless fuel system. This design reduces vapor emissions and maintains a steady pressure supply to the injectors.
Operation and Performance
When the ignition is switched on, the electric motor inside the pump activates and pressurizes the fuel line. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) monitors fuel pressure and adjusts the pump’s operation accordingly. In modern Volvo models, especially those with turbocharged engines, the system may include a high-pressure fuel pump (HPFP) in addition to the in-tank low-pressure pump. This ensures that fuel reaches the injectors at extremely precise pressures for optimal performance and emissions control.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Typical issues with these pumps include:
- Low fuel pressure due to motor wear or blockage.
- No-start conditions from pump failure or relay malfunction.
- Fuel contamination causing premature wear on the impeller.
To prolong fuel pump life, it’s advised to keep the fuel tank above one-quarter full, replace the fuel filter periodically, and use clean, high-quality fuel.
Conclusion
The fuel pump in the Mazda 3, Ford Focus, and Volvo models exemplifies advanced engineering that balances efficiency, reliability, and safety. As a vital part of the vehicle’s fuel delivery system, proper maintenance and timely replacement of the pump ensure smooth engine performance, improved fuel economy, and long-term durability.
